In the realm of global healthcare, ensuring safety during injections is a cornerstone of public health. Among the critical innovations in this field is the auto disable syringe—a specialized medical tool designed to address one of the most pressing risks in medical procedures: the reuse of syringes. As a vital part of modern medical consumables, understanding what an AD syringe is, how it differs from traditional options, and its role in healthcare systems worldwide is essential for professionals in medical supply chains, healthcare facilities, and public health initiatives.
What Is an Auto Disable Syringe?
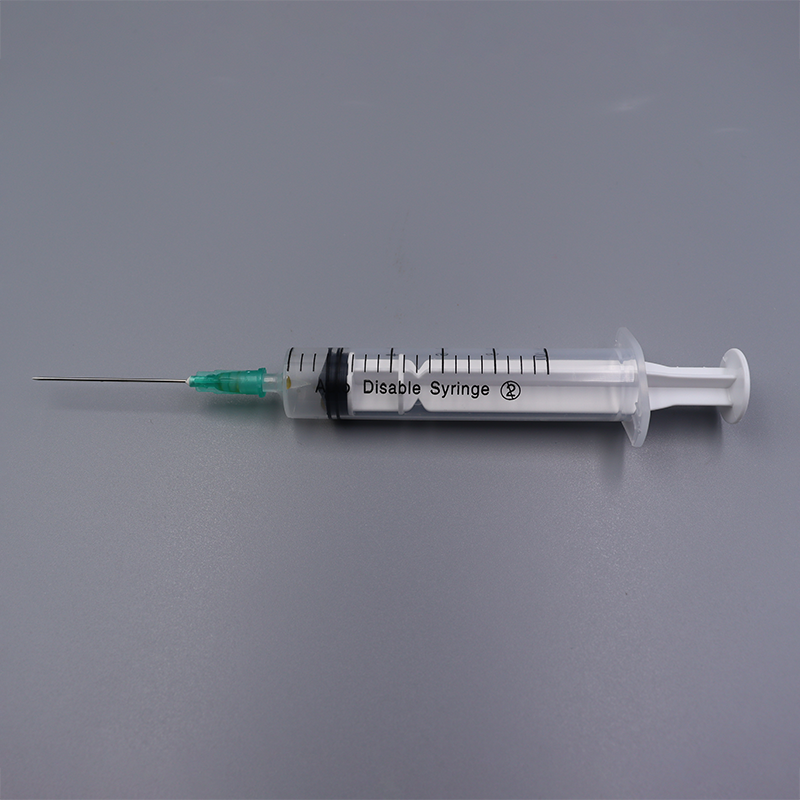
An auto disable (AD) syringe is a single-use disposable syringe engineered with a built-in mechanism that permanently disables the device after one use. Unlike standard disposable syringes, which rely on user discipline to prevent reuse, an AD syringe automatically locks or deforms after the plunger is fully depressed, making it impossible to draw or inject fluid a second time.
This innovation was developed in response to the alarming spread of bloodborne diseases—such as HIV, hepatitis B, and C—caused by the reuse of syringes in resource-limited settings or due to human error. Today, auto disable syringes are recognized as a gold standard in immunization programs, maternal health initiatives, and any medical scenario where preventing cross-contamination is critical. As a key medical consumable, they are widely integrated into global medical supply chains to enhance patient and healthcare worker safety.
Auto-Disable Syringe vs. Normal Syringe: Key Differences
To appreciate the value of AD syringes, it’s important to contrast them with standard disposable syringes:
Reuse Risk: A normal disposable syringe is designed for single use but lacks built-in safeguards. In busy clinics or regions with limited medical supplies, cost-cutting measures or oversight can lead to accidental or intentional reuse. An auto disable syringe, by contrast, eliminates this risk entirely through its mechanical design.
Mechanism: Standard syringes rely on a simple plunger-and-barrel structure that allows repeated operation if cleaned (though this is never safe). AD syringes add a locking feature—often a clip, spring, or deformable component—that activates once the plunger reaches the end of its stroke, rendering the plunger immovable.
Regulatory Alignment: Many global health organizations, including the World Health Organization (WHO), recommend auto disable syringes for vaccinations and high-risk injections. Normal disposable syringes do not meet these strict safety standards, making AD syringes a non-negotiable in compliant medical supply networks.
Cost vs. Long-Term Value: While AD syringes may have a slightly higher upfront cost than basic disposable syringes, their ability to prevent costly disease outbreaks and reduce healthcare burdens makes them a cost-effective choice in the long run—especially in large-scale immunization campaigns.
Benefits of Auto Disable Syringes
The adoption of auto disable syringes brings multifaceted advantages to healthcare systems, patients, and communities:
Eliminates Cross-Contamination: By preventing reuse, AD syringes drastically reduce the risk of transmitting pathogens between patients. This is particularly critical in regions with high rates of infectious diseases, where a single reused syringe can spark outbreaks.
Enhances Healthcare Worker Safety: Healthcare providers are often at risk of accidental needle sticks when disposing of used syringes. The locked plunger in AD syringes ensures the device is inert, minimizing handling hazards during waste management.
Compliance with Global Standards: Organizations like UNICEF and the WHO mandate auto disable syringes for vaccine administration in their programs. Using these tools ensures alignment with international medical consumables regulations, easing access to global medical supply networks.
Reduces Medical Waste Risks: Unlike normal syringes, which may be improperly reused before disposal, AD syringes are guaranteed to be single-use. This simplifies waste tracking and reduces the burden on medical waste treatment facilities.
Builds Public Trust: In communities where fear of unsafe injections discourages participation in vaccination drives, auto disable syringes provide visible proof of safety, boosting compliance with public health initiatives.
Auto Disable Syringe Mechanism: How It Works
The magic of an auto disable syringe lies in its innovative engineering. While designs vary slightly by manufacturer, the core mechanism revolves around irreversible plunger movement:
Plunger and Barrel Integration: The plunger of an AD syringe features a weak point or a locking tab that interacts with the inner barrel. When the plunger is pushed to deliver the full dose, this tab either breaks, bends, or engages with a ridge inside the barrel.
Irreversible Locking: Once activated, the plunger can no longer be pulled back to draw fluid. In some models, the plunger may even detach from its rod, ensuring it cannot be repositioned. This mechanical failure is intentional and permanent.
Visual Confirmation: Many AD syringes are designed to show a clear visual cue—such as a protruding tab or a bent plunger—indicating that the device has been used and disabled. This helps healthcare workers quickly verify safety.
This mechanism is robust enough to withstand intentional tampering, making AD syringes reliable even in challenging environments where medical supplies may be scarce or mismanaged.
Auto Disable Syringe Uses
Auto disable syringes are versatile tools with applications across various healthcare scenarios, solidifying their role as essential medical consumables:
Vaccination Programs: They are the preferred choice for childhood immunizations (e.g., polio, measles, and COVID-19 vaccines) due to their ability to prevent reuse in mass campaigns.
Infectious Disease Treatment: In settings treating HIV, hepatitis, or other bloodborne illnesses, AD syringes prevent accidental exposure and transmission.
Maternal and Child Health: During childbirth or neonatal care, where sterility is critical, these syringes reduce risks for both mothers and infants.
Low-Resource Settings: In regions with limited access to medical supplies or training, AD syringes act as a fail-safe against improper reuse, protecting vulnerable populations.
Dental and Veterinary Care: Beyond human medicine, they are used in dental procedures and animal health to maintain sterility and prevent disease spread.
Conclusion
The auto disable syringe represents a pivotal advancement in medical consumables, merging safety, reliability, and ease of use to protect global public health. By eliminating the risk of reuse, it addresses a critical gap in healthcare safety, particularly in regions dependent on consistent medical supply chains.
For medical supply companies and healthcare providers, prioritizing AD syringes is not just a compliance measure—it’s a commitment to reducing preventable diseases and building resilient healthcare systems. As the world continues to face public health challenges, the role of auto disable syringes in safeguarding communities will only grow more indispensable.
Post time: Jul-29-2025