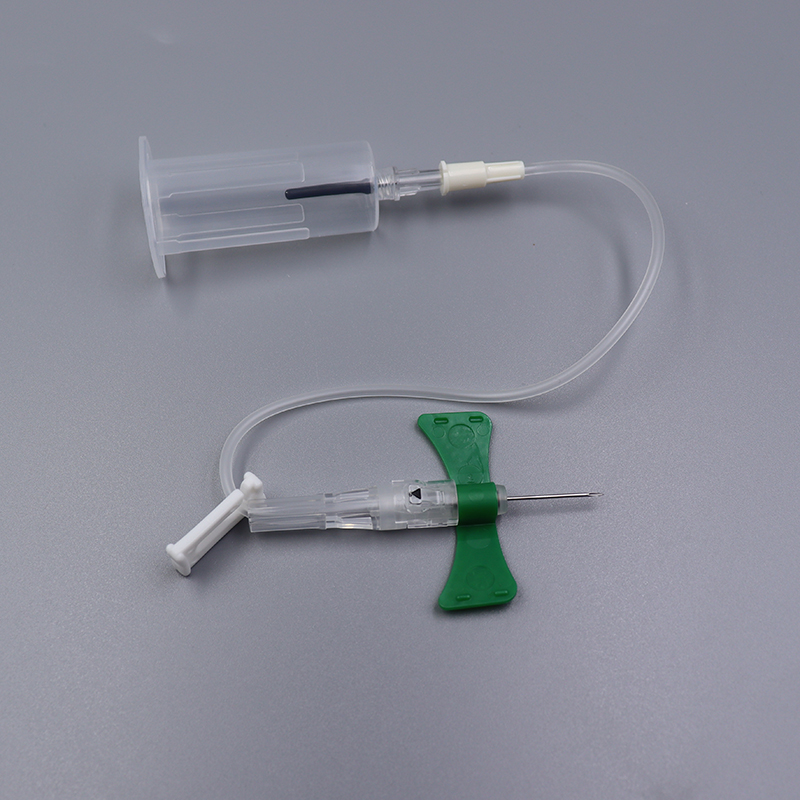
In modern healthcare, patient safety and caregiver protection are top priorities. One often-overlooked but critical piece of equipment—the butterfly needle—has undergone a significant transformation in recent years. Traditional butterfly needles, while widely used for IV access and blood collection, pose risks such as accidental needlestick injuries, operational inefficiencies, and discomfort during repeated insertions. This has led to the development of a smarter, safer alternative: the retractable butterfly needle.
Understanding the Retractable Butterfly Needle
Definition and Variants
A retractable butterfly needle is an enhanced version of the traditional butterfly needle, featuring a built-in mechanism that allows the needle tip to retract either manually or automatically after use. This innovative design aims to minimize needlestick injuries, improve user control, and reduce patient discomfort.
Retractable butterfly needles maintain the classic design—flexible wings, a thin hollow needle, and tubing—but incorporate a retractable needle core that withdraws into the protective sheath. Based on the retraction mechanism, these devices are typically classified as:
-
Manual retraction types (button-push or slide-lock design)
-
Automatic spring-loaded types
-
Application-specific designs: pediatric use, IV infusion, or blood collection.
Key Differences from Traditional Butterfly Needles
-
Enhanced Safety: The retraction mechanism ensures the needle tip is safely concealed after use, reducing the risk of accidental injury or exposure to bloodborne pathogens.
-
Improved Usability: Some models support one-handed retraction, allowing medical staff to maintain better control and reduce procedural complexity.
How Retractable Butterfly Needles Work
Mechanical Structure and Workflow
The core functionality of a retractable butterfly needle lies in its internal spring or locking mechanism, which engages after use to pull the needle back into its housing.
-
Needle Cannula: Usually stainless steel, encased in a soft plastic sheath.
-
Retraction Core: Spring or elastic mechanism attached to the needle shaft.
-
Trigger System: May be a press button, slider, or pressure-sensitive latch.
How It Works:
-
The needle is inserted with wings held between fingers.
-
After successful venipuncture or infusion, the trigger mechanism is activated.
-
The needle tip retracts into the housing, locking securely inside.
Using a Retractable Butterfly Needle: Step-by-Step Guide
Indications and Contraindications
-
Ideal for: Pediatric IV access, blood draws in uncooperative patients, rapid emergency access, and outpatient settings.
-
Avoid in: Inflamed or infected sites, very thin or fragile veins (e.g., chemotherapy patients), or patients with coagulation disorders (risk of bruising upon retraction).
Standard Procedure
-
Preparation:
-
Verify patient details and confirm vein location.
-
Disinfect site with iodine or alcohol (≥5cm radius).
-
Inspect packaging, expiration date, and trigger mechanism.
-
-
Insertion:
-
Hold wings, bevel up.
-
Insert at a 15°–30° angle.
-
Lower to 5°–10° upon flashback confirmation and advance slowly.
-
-
Retraction:
-
Manual model: Hold wings, press button to trigger spring retraction.
-
Automatic model: Push wings to a locked position, triggering needle withdrawal.
-
-
Post-Use:
-
Detach tubing from device.
-
Apply pressure to puncture site.
-
Dispose of device in sharps container (no recapping needed).
-
Tips & Troubleshooting
-
Pediatric use: Pre-fill tubing with saline to reduce insertion resistance.
-
Elderly patients: Use 24G or smaller gauge to avoid vascular trauma.
-
Common issues:
-
Poor blood return → adjust needle angle.
-
Retraction failure → ensure full trigger depression and check expiration.
-
When and Why to Retract the Butterfly Needle
Routine Timing
-
Immediately after infusion or blood draw to prevent needle shift and accidental sticks.
-
In unpredictable settings (e.g., with children or confused patients), preemptively retract upon detecting risk of movement.
Special Scenarios
-
Failed puncture: If the first attempt misses the vein, retract and replace the needle to prevent tissue damage.
-
Unexpected symptoms: Sudden pain or infiltration during use—stop, retract, and assess the vein integrity.
The Benefits of Retractable Butterfly Needles
Superior Safety
Clinical studies indicate that retractable butterfly needles reduce needlestick injury rates by up to 70%, particularly in busy hospital environments. They also help prevent accidental injuries in pediatric patients who may flail or grab the exposed needle.
Efficiency and Workflow
-
Single-hand operation allows for faster, more efficient procedures.
-
Eliminates the need for extra safety accessories like needle caps or sharps boxes in mobile scenarios.
Improved Patient Comfort
-
Reduced pain from needle withdrawal, especially for children.
-
Psychological relief knowing the needle disappears quickly after use.
Broader Applications
-
Suitable for use in fragile patients (geriatric, oncology, or hemophilia cases).
-
Helps prevent repeated punctures by enabling more controlled needle insertion and removal.
Conclusion & Future Outlook
Conclusion: The retractable butterfly needle represents a major advancement in medical consumables. Its intelligent design tackles the dual challenge of safety and usability, offering significant improvements over traditional models in clinical efficiency and patient comfort.
Looking Ahead: Continued innovation in this space may bring smarter activation systems, biodegradable components to reduce medical waste, and sensor-assisted feedback for optimal depth placement. While cost and training remain barriers to universal adoption, the trend toward safer needle technologies is clear and irreversible.
Post time: Jul-21-2025